Why Is My Digital Multimeter Reading Half Dc Voltage?
Eugene is a qualified control/instrumentation engineer Bsc (Eng) and has worked as a developer of electronics & software for SCADA systems.
What is a Multimeter?
Multimeters are widely used by professionals in several fields including industrial maintenance and testing, enquiry, apparatus repair and electric installation. However a digital multimeter or DMM is also an invaluable test instrument for home and DIY use. The musical instrument tin can used for measuring voltage, current and resistance and tin cheque:
- Battery voltages
- Vehicle electrics and electronics
- Continuity of cables and power cords
- Home appliances and electronic devices
- Fuses
Volts, Amps, Ohms - What Does it All Mean?
Before we learn how to use a multimeter, nosotros demand to become familiar with the quantities nosotros are going to be measuring. The nearly basic excursion we'll encounter is a voltage source, which could be connected to a load. The voltage source could be a battery or a mains power supply. The load might exist a device such as a seedling or electronic component called a resistor. The circuit tin be represented by a diagram called a schematic. In the circuit beneath, the voltage source 5 creates an electrical pressure which forces a electric current I to flow in a loop around the circuit and through the load R. Ohm's Law tells usa that if we split the voltage 5 by the resistance R, measured in ohms, it gives us a value for the current I in amps:
Current I = 5/R
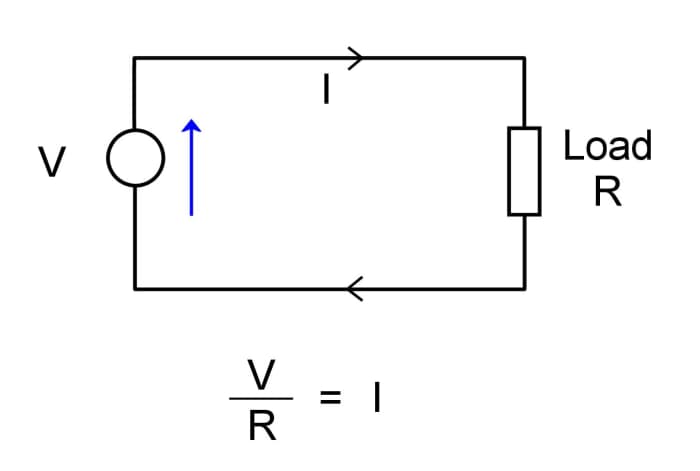
Schematic of a uncomplicated circuit.
© Eugene Brennan
Instance:
A 12 volt car battery is continued to a load with a resistance of iv ohms. What is the current?
I = V/R
5 = 12 volts
R = iv ohms
So electric current I = 12/iv = 3 amps
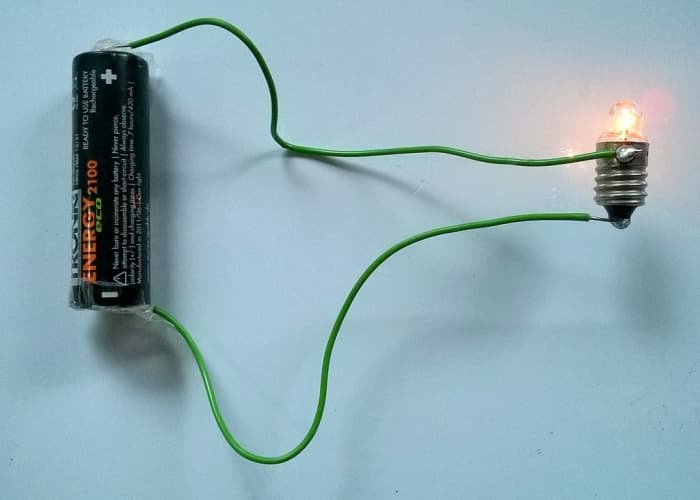
A simple circuit consisting of an AA cell and a seedling. The AA prison cell is the voltage source that causes current to flow in a loop around the circuit and through the bulb.
© Eugene Brennan
For more detailed information on electric current, voltage and resistance, AC and DC, take a detour to my other article:
Watts, Amps, Volts, Kilowatt Hours (kWh) and Electric Appliances - Bones Electricity Explained
What Does a Multimeter Measure?
A basic multimeter allows you to measure the post-obit:
- DC voltage
- DC current
- AC voltage
- AC current (not all basic meters have this function)
- Resistance
- Continuity - indicated past a buzzer or tone
In addition meters may have the following functions:
- Capacitance measurement
- Transistor HFE or DC current gain
- Temperature measurement with an additional probe
- Diode examination
- Frequency measurement
The value measured by the instrument is indicated on an LCD display or scale.
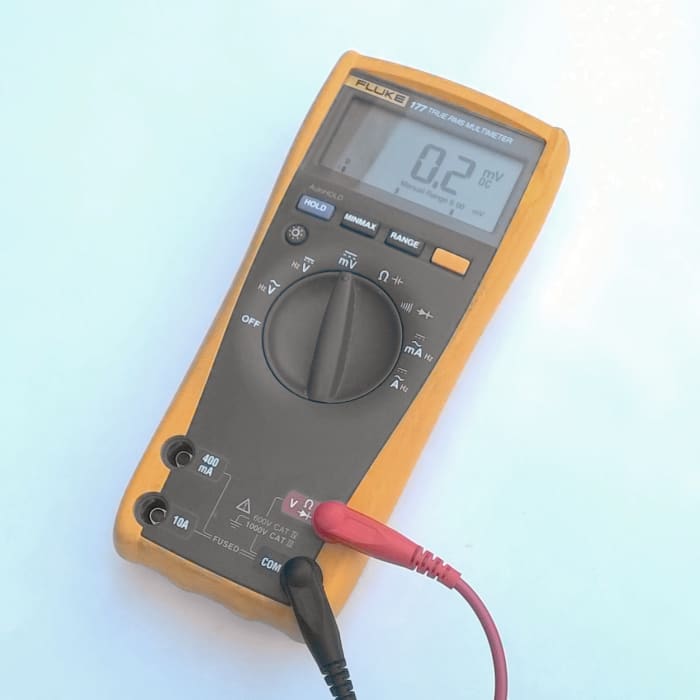

A professional model 177 Fluke multimeter with an accuracy of 0.09 % on DC volts.
© Eugene Brennan
Read More From Dengarden
Parts of a Meter
- The Display. This is usually a multidigit, vii segment LCD display. Some laboratory instruments however have LED displays which are easier to read under certain lighting conditions.
- Rotary Range Selector Dial. This allows you to select the function which you will be using on the meter. On a not-autoranging meter, it likewise selects the range.
- Connection Ports. These are 4mm diameter female person sockets into which 4 mm probe leads are plugged.
- Probes. These take a pointed tip on 1 end for touching against the bespeak of measurement and a plug on the other end for insertion into a connection socket.

A range selector dial is used to select the function (volts, amps, resistance) and range. Annotation the symbols used for Ac and DC. Meet graphic further down this article for an explanation.
Original unannotated epitome public domain via Pixabay.com
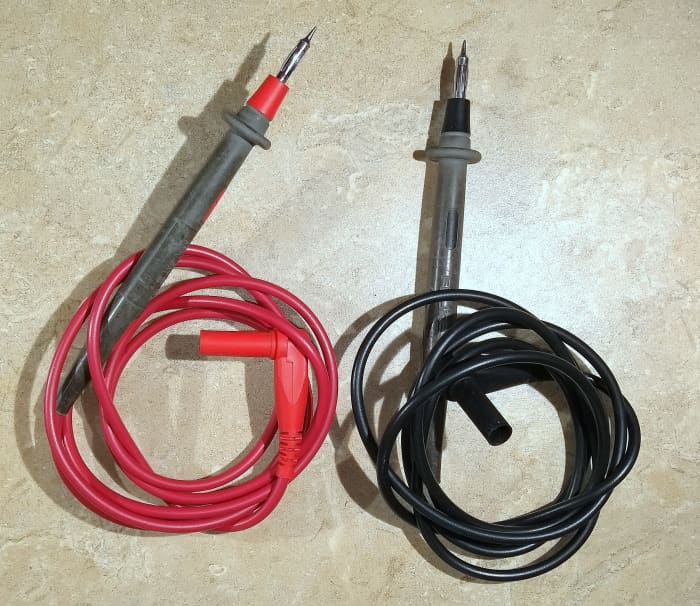

Multimeter probes.
© Eugene Brennan

4mm plug on the end of a multimeter probe.
© Eugene Brennan
Connexion Sockets on a Meter
The arrangement is non-standard and depends on the make/model of meter, so it's important to understand the office of each socket to avoid damage to the meter:
- Com is the mutual socket into which the black probe lead is plugged. This is standard on all meters.
- VΩmA marked on a socket indicates that the red probe lead is plugged into it for measuring voltage, resistance or depression electric current ("mA" means "milliamps"). If at that place is no mention of "mA" on this socket, in that location will be i or more split up sockets for connecting the probe pb to measure current. These sockets will be marked "A" or "mA" with the max current range (east.g. 10A for loftier current readings and 400 mA for lower electric current readings).
How Practice I Setup a Multimeter to Measure Volts, Amps or Ohms?
Voltage, electric current and resistance ranges are commonly set past turning a rotary range selection dial. This is set to the quantity being measured, e.1000. AC volts, DC volts, Amps(current) or Ohms (resistance).
If the meter is non-autoranging, each function will have several ranges. So for example, the DC volts function range volition have 1000V, 200V , 20V, 2V and 200mV ranges. Using the lowest range possible gives more significant figures in the reading.
How to Measure Voltage
- Power off the circuity/wiring nether test if there is a danger of shorting out closely spaced adjacent wires, terminals or other points which have differing voltages.
- Plug the black ground probe pb into the COM socket on the meter (run across photograph below).
- Plug the red positive probe pb into the socket marked Five (usually also marked with the Greek alphabetic character "omega" Ω and peradventure a diode symbol).
- If the meter has has a transmission range option dial, turn this to select AC or DC volts and pick a range to give the required accuracy. So for instance measuring 12 volts on the 20 volt range will give more decimal places than on the 200 volt range.
If the meter is autoranging, plough the dial to the 'V' setting with the symbol for Air conditioning or DC (see "What Do the Symbols on the Range Punch Hateful?" below). - A multimeter must be connected in parallel in a circuit (run across diagram beneath) in club to mensurate voltage. So this means the 2 test probes should exist connected in parallel with the voltage source, load or any other 2 points beyond which voltage needs to be measured.
- Touch the blackness probe against the first point of the circuitry/wiring.
- Power upward the equipment.
- Touch the other ruby-red probe against the second betoken of test. Ensure you don't bridge the gap between the bespeak being tested and adjacent wiring, terminals or tracks on a PCB.
- Take the reading on the LCD display.
Note: A lead with a 4mm banana plug on one end and a crocodile clip on the other stop is very handy. The croc clip can be connected to basis in the circuit, freeing upward ane of your hands.
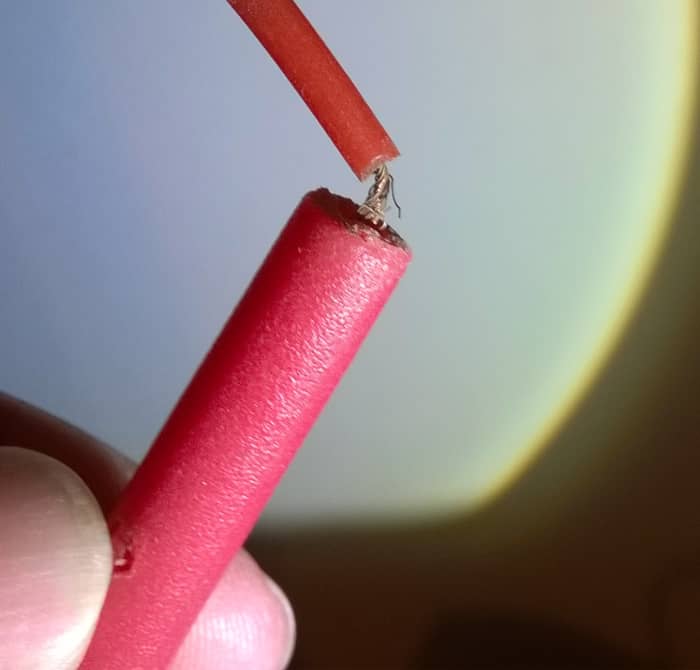
Exposed conductor of test lead
© Eugene Brennan
Connecting Probe Leads to Measure Voltage
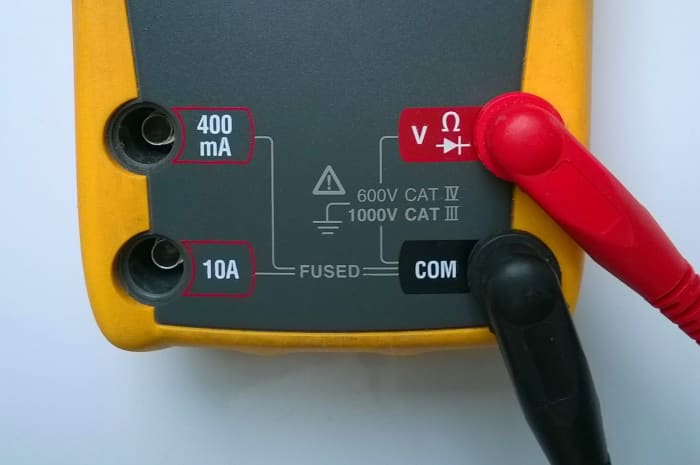

Test leads and 4mm sockets on a DMM, setup to measure voltage
© Eugene Brennan
Serial and Parallel Connections
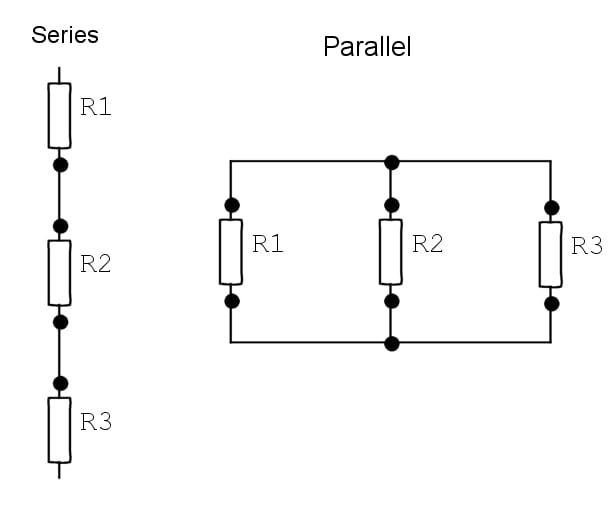
Explaining serial and parallel connections (R1, R2 and R3 are resistors)
© Eugene Brennan
Measuring Voltage - Meter in Parallel With Load or Voltage Source
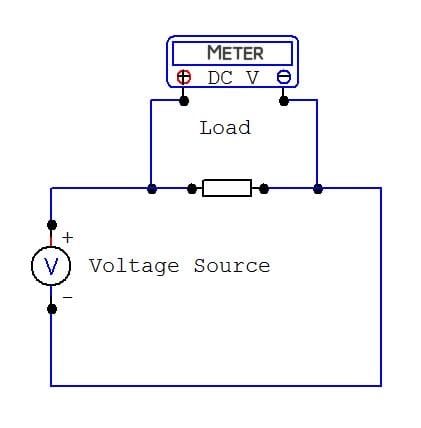
DMM connected in parallel with load to measure voltage across information technology
© Eugene Brennan
Choosing Examination Probes
Virtually meters come up as standard with pointed, needle tip probes. An culling is crocodile (alligator) probes that have leap loaded clips. These are useful so that one or both probes tin can be connected to a circuit without holding the probes in place by hand.
Safety Showtime When Measuring Mains Voltages!
- Before using a meter to measure out mains voltages, visually inspect it first. Bank check the meter, probes and accessories are gratis from damage. Never use test leads with exposed conductors which could exist touched inadvertently or a meter with cracks in the casing or exposed metal. Brand sure probes are pushed securely into sockets.
- Only use meters and test leads that have a CAT rating suitable for the measuring job. Cull leads with proper insulation, finger guards and shrouded plugs.
Fluke has a safety guide here giving more data on safe multimeter use.
- Double check that test leads are plugged into the common and voltage sockets of the DMM (see photograph beneath) and not the current sockets. This is essential to avoid blowing up the meter.
- Ready the range dial on the meter to Air conditioning volts and the highest voltage range.
- Ideally use test leads with shrouded crocodile clips on the ends, power off the circuit, connect the leads and power upwards again so y'all don't accept to hold leads. TV repair technicians used to have a saying that the safest place to proceed one of your easily is in your pocket when making measurements. When holding a probe in each hand, there'due south always the danger of making contact with neutral or basis with i hand and hot (live) with the other if the probe or leads are damaged, resulting in a daze across the heart, a potentially lethal scenario. Alternatively the negative probe lead can exist connected to neutral using a crocodile connector and then that measurements can be taken with one hand using the positive needle probe.
- If you have to measure voltage at a socket outlet, turn off power earlier inserting probe tips. If this isn't possible, ever insert the probe tip into the neutral terminal of the outlet starting time and and then insert the other probe into the live (hot) final. If yous insert the probe tip into the hot first and inadvertently touch the tip of the other probe, or it makes contact with a metal surface, you can get a daze or potentially exist electrocuted.
Meter and Measurement Rubber Categories
Ideally purchase and use a meter with a to the lowest degree Cat Three or preferably True cat IV protection for testing mains voltages. This blazon of meter will incorporate high rupturing chapters (HRC) fuses and other internal prophylactic components that offer the highest level of protection against overloads and transients on the line being tested. A meter with less protection tin potentially blow up causing injury if it is connected incorrectly, or a transient voltage generates an internal arc.
Autoranging Meters
Autoranging meters notice the magnitude of the voltage and select the range automatically to give the nigh amount of meaning digits on the display. Y'all must nevertheless set the manner to resistance, volts or current and besides connect the probe leads to the proper sockets when measuring current.
What Practise the Symbols on the Range Dial Hateful?

Symbols used on an autoranging DMM
© Eugene Brennan
Identifying Live or Hot Wires
This Fluke "VoltAlert™" non-contact voltage detector from Amazon is a standard tool in any electricians tool kit, but useful for homeowners also. I employ 1 of these for identifying which conductor is live whenever I'm doing any home maintenance. Unlike a neon screwdriver tester (stage tester), you can use i of these in situations when live parts/wires are shrouded or covered with insulation and you can't make contact with wires. It likewise comes in useful for checking whether at that place'south a break in a power flex and where the break occurs.
Note: It'southward always a good idea to utilize a neon tester to double check that power is definitely off when doing any electrical maintenance.
How to Measure Current
- Plow off the ability in the circuit being measured.
- Connect the probe leads every bit shown in the photo below. Plug the black basis probe atomic number 82 into the COM socket.
- Plug the carmine positive probe lead either into the mA socket or the high current socket which is usually marked 10A (some meters have a xx A socket instead of 10A). The mA socket is often marked with the maximum current and if you estimate that the current will be greater than this value, you must use the 10 A socket, otherwise you will stop upward blowing a fuse in the meter. On some meters, there is no additional socket for measuring current and the same socket is used as for measuring voltage (ordinarily marked VΩmA).
- A multimeter must be inserted in series in a circuit in order to measure current. Run into the diagram below.
- Turn the punch on the meter to the highest current range (or the 10A range if the probe is in the 10A socket). If the meter is autoranging, set it to the "A" or mA setting. (Meet the photo above for an caption of symbols used).
- Plough on the power.
- If the range is too high, you tin can switch to a lower range to get a more authentic reading.
- Remember to return the positive probe to the V socket when finished measuring current. The meter is practically a brusk excursion when the lead is in the mA or x A socket. If you forget and connect the meter to a voltage source when the lead is in this position, you may end up blowing a fuse at best or blowing up the meter at worst! (On some meters the 10A range is un-fused).
Connecting Probe Leads to Measure Electric current

Test leads and sockets on a DMM, setup to measure current
© Eugene Brennan
Measuring Current - Meter in Serial
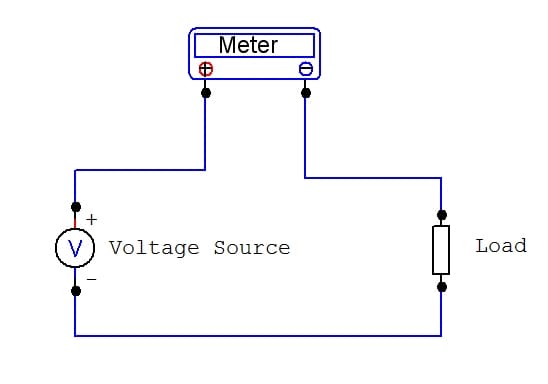
DMM connected in serial with load to measure current flowing through it
© Eugene Brennan
What Multimeter Should I Purchase? Recommended Products From Amazon
Fluke, a leading Us manufacturer of digital instrumentation, promotes the Fluke 113 model for general purpose employ in the home or for car maintenance. This is an first-class meter and can measure AC and DC volts, resistance, check continuity and diodes. The meter is auto-ranging, then ranges don't have to exist fix. Information technology is too a true-RMS meter. It doesn't measure electric current, so If yous need to measure AC and DC electric current, the Fluke 115 has this added facility.
An alternative is the Fluke 177 model which is a high accuracy instrument (the specification is 0.09% accurateness on DC volts). I use this model for more authentic testing and professional utilize and it tin can measure Air-conditioning and DC voltage and current, resistance, frequency, capacitance, continuity and diode test. It can likewise indicate max and min values on each range.
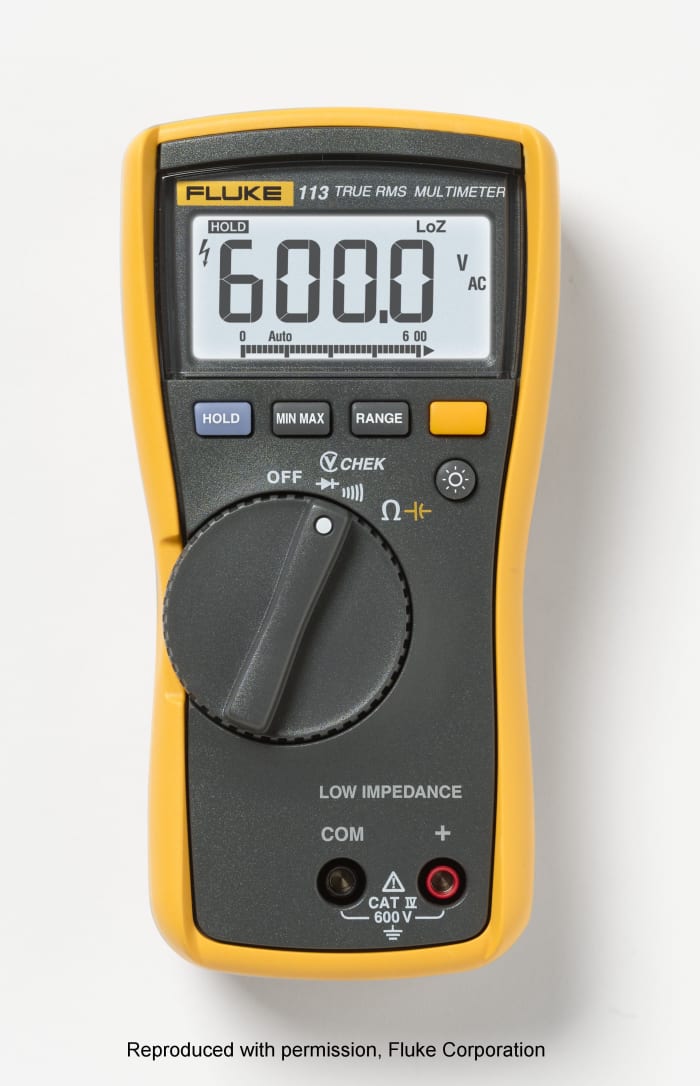

Fluke 113 general purpose true RMS digital multimeter.
Epitome reproduced with permission from Fluke Corporation
Fluke 177 Multimeter with Motorcar-Ranging Facility
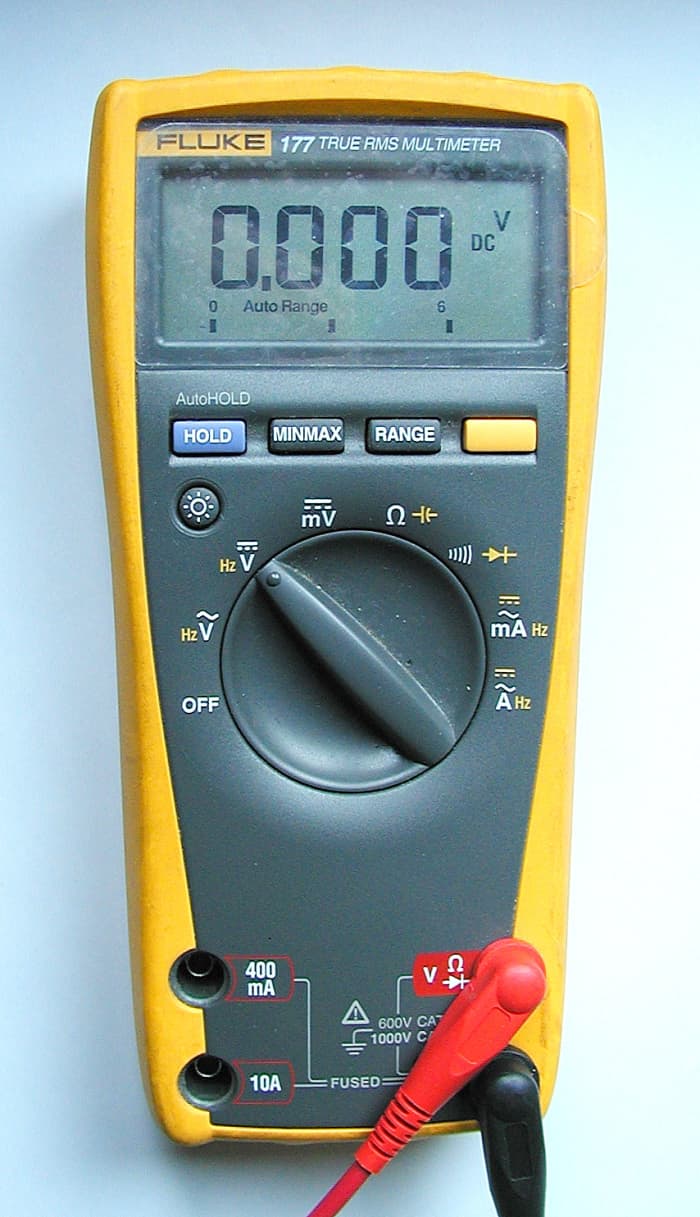

This autoranging multimeter from Fluke, a leading manufacturer of electronic test equipment, has an accuracy of 0.09% on DC ranges. It besides has True cat Four protection to 600volts
© Eugene Brennan
Measuring Big Currents with a Clamp Meter (Tong Tester)
On near multimeters, the highest current range is x or 20 amps. It would exist impractical to feed very high currents through a meter because normal 4 mm sockets and examination leads wouldn't be capable of conveying loftier currents without overheating. Instead, clamp meters are used for these measurements.
Clamp meters (every bit the proper name suggests), also known as tong testers, accept a spring loaded clench like a giant clothes peg which clamps around a current carrying cable. The advantage of this is that a circuit doesn't have to broken to insert a meter in series, and power needn't be turned off as is the case when measuring electric current on a standard DMM. Clamp meters use either an integrated current transformer or hall effect sensor to mensurate the magnetic field produced by a flowing current. The meter tin can be a self contained instrument with an LCD which displays current, or alternatively the device tin output a voltage signal via probe leads and 4mm "assistant" plugs to a standard DMM. The voltage is proportional to the measured betoken, typically 1mv represents 1 amp.
Clench meters can measure hundreds or thousands of amps.
To apply a electric current clamp, y'all just clamp over a single cablevision. In the example of a ability string or multicore cable, you demand to isolate one of the cores. If ii cores conveying the same current but in opposite directions are enclosed inside the jaws (which would exist the situation if you clench over a power cord), the magnetic fields due to the electric current period would cancel out and the reading would be nix.
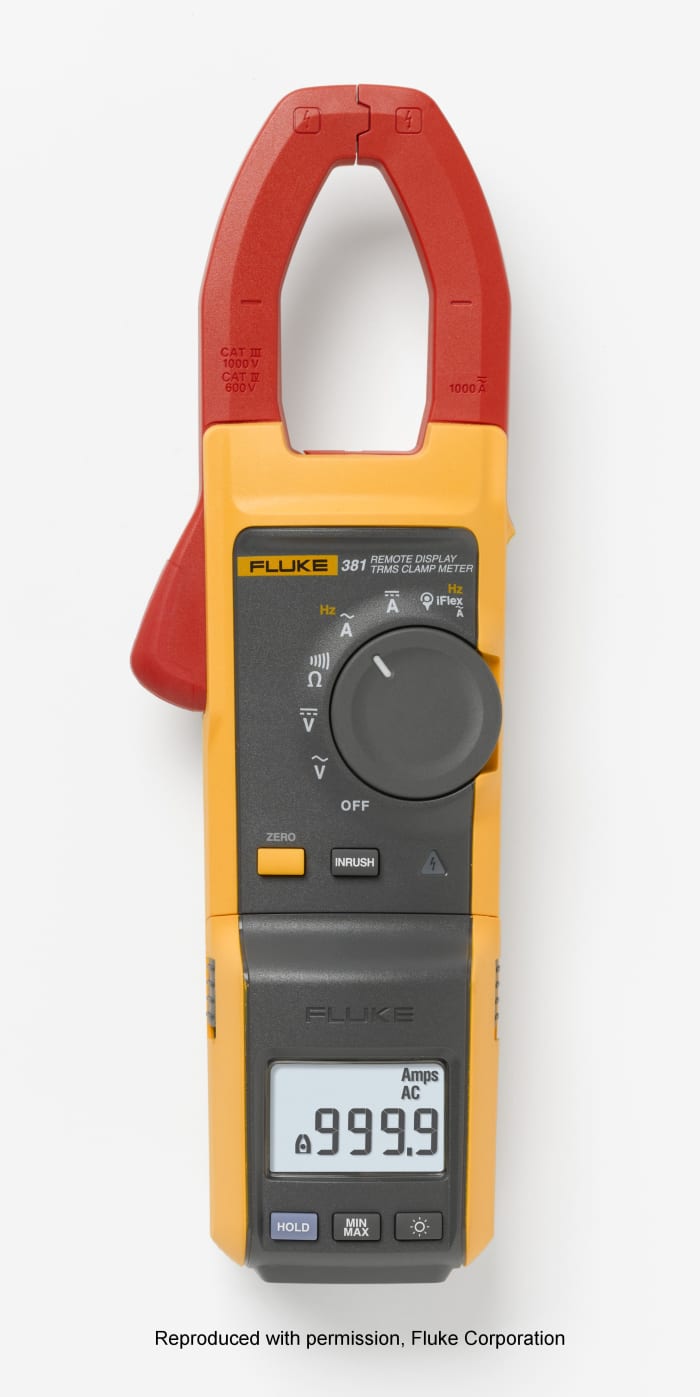

Fluke 381 True RMS Air conditioning/DC clamp meter
Epitome reproduced with permission from Fluke Corporation
How to Measure Resistance
- If the component is on a circuit board or in an appliance, plow off the ability
- Disconnect one end of the component if it'south in a circuit. This may involve pulling off spade leads or desoldering. This is important equally there may be other resistors or other components having resistance, in parallel with the component being measured.
- Connect the probes as shown in the photo below.
- Turn the dial to the lowest Ohm or Ω range. This is likely to exist the 200 ohm range or similar.
- Place a probe tip at each stop of the component being measured.
- If the brandish indicates "one", this means that resistance is greater than tin can be displayed on the range setting yous have selected, and so you must turn the dial to the next highest range. Echo this until a value is displayed on the LCD.
Connecting Probe Leads to Measure Resistance
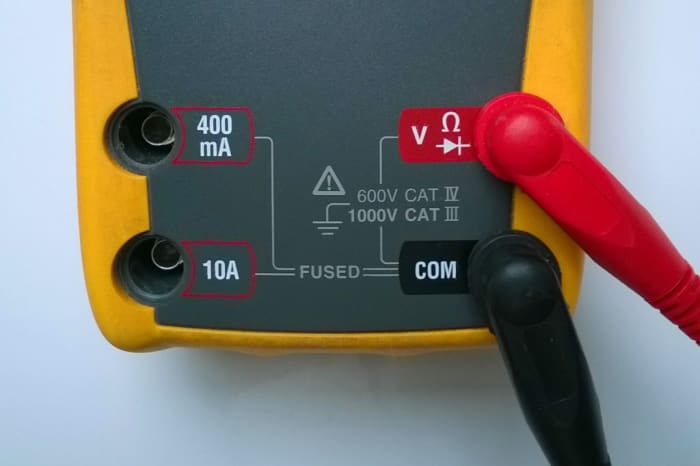

Leads setup to measure resistance
© Eugene Brennan
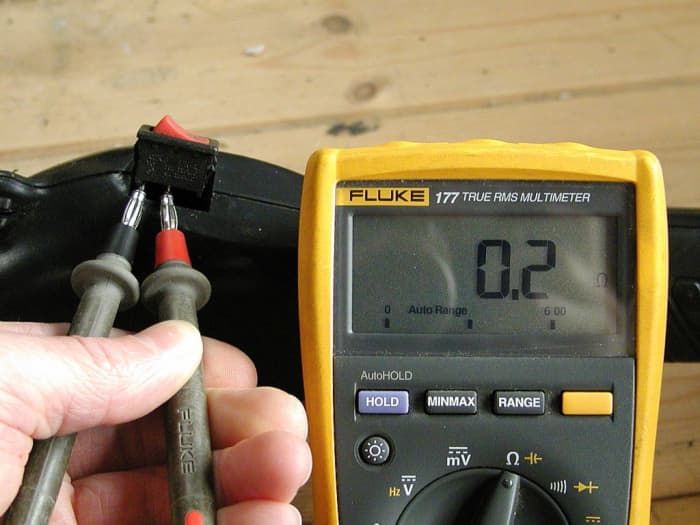

Check resistance across switch contacts
© Eugene Brennan
How to Check Continuity and Fuses
A multimeter is useful for checking breaks in flexes of appliances, blown filaments in bulbs and blown fuses, and tracing paths/tracks on PCBs
- Turn the selecting dial on the meter to the continuity range. This is frequently indicated by a symbol which looks similar a series of arcs of a circle (See the photograph showing symbols used on meters above).
- Connect the probe leads to the meter equally shown in the photo below.
- If a conductor on a excursion lath/ a wire in an appliance needs to be checked, make certain the device is powered downwards.
- Identify the tip of a probe at each end of the conductor or fuse which needs to be checked.
- If resistance is less than well-nigh thirty ohms, the meter will indicate this by by a beep tone or buzzing sound. The resistance is usually indicated on the display also. If there is break in continuity in the device being tested, an overload indication, commonly the digit "one", will be displayed on the meter.
Connecting Probe Leads to Check Diodes or Continuity
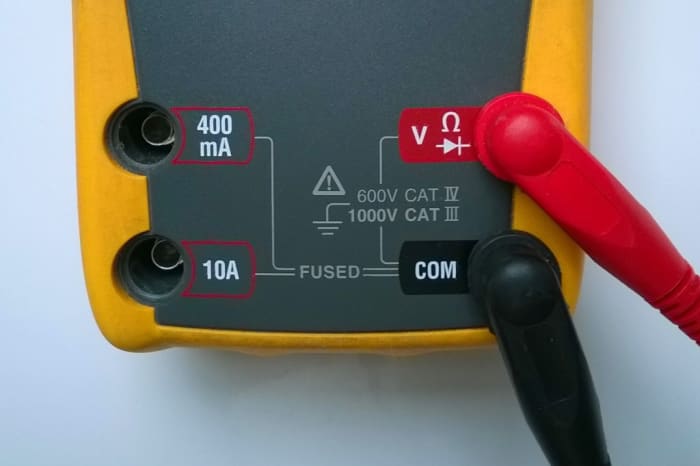

Leads setup to check diodes or continuity
© Eugene Brennan
How to Cheque Diodes
A multimeter tin can be used to check whether a diode is curt circuited or open up circuited. A diode is an electronic 1 mode valve or check valve, which merely conducts in one direction. A multimeter when connected to a working diode indicates the voltage across the component.
- Turn the punch of the meter to the diode test setting, which is indicated by a triangle with a bar at the end (see the photograph showing symbols used on meters in a higher place).
- Connect the probes as shown above.
- Touch the tip of the negative probe to one end of the diode, and the tip of the positive probe to the other end.
- When the black probe is in contact with the cathode of the diode (commonly indicated by a bar marked on the component) and the cherry probe makes contact with the anode, the diode conducts, and the meter indicates the voltage. This should exist almost 0.vi volts for a silicon diode and about 0.2 volts for a Schottky diode. When the probes are reversed, the meter should indicate a "1" because the diode is open circuit and non-conducting.
- If the meter reads "1" when the probes are placed either way, the diode is likely to be faulty and open circuit. If the meter indicates a value close to naught, the diode is shorted circuited.
- If a component is in circuit, resistances in parallel will affect the reading and the meter may not indicate "one" but a value somewhat less.
How to Measure Wattage and the Power Consumption of an Appliance With a Multimeter
Watts = Volts x Current
So to measure out the ability in watts of a load/appliance, both the voltage across the load and the current passing through information technology must be measured. If you take two DMMs, you tin can measure the voltage and current simultaneously. Alternatively measure out the voltage first, and so disconnect the load so that the DMM can exist inserted in series to mensurate electric current. When whatever quantity is measured, the measuring device has an influence on the measurement. Then the resistance of the meter will reduce current slightly, and give a lower reading than the actual value with the meter not connected.
3 means to measure current drawn past an electrical appliance:
- The safest way to measure the power consumption of an appliance powered from the mains is to utilise a power adapter. These devices plug into a socket and the appliance is and so plugged into the adapter which displays information on an LCD. Typical parameters displayed are voltage, current, power, kwh, toll and how long the appliance was turned on (useful for fridges, freezers and air conditioners which cut in and out). You can read more almost these gadget in my article here:
Checking Power Consumption of Appliances With an Energy Monitoring Adapter - An culling way of safely measuring electric current drawn by an electrical appliance is to brand upwards a exam atomic number 82 using a short slice of power cord with a trailing socket on 1 finish and a mains plug on the other. The inner neutral core of the ability cord could exist freed and separated from the outer sheath, and current measured with a clamp meter or probe (Don't remove the insulation!)
Only make connections and conform range on the meter with the power off!
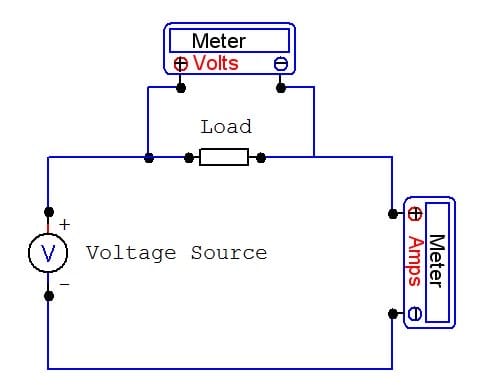
Measuring watts = volts x amps. Ane meter measures voltage across the load. The other meter measures electric current flowing through it.
© Eugene Brennan
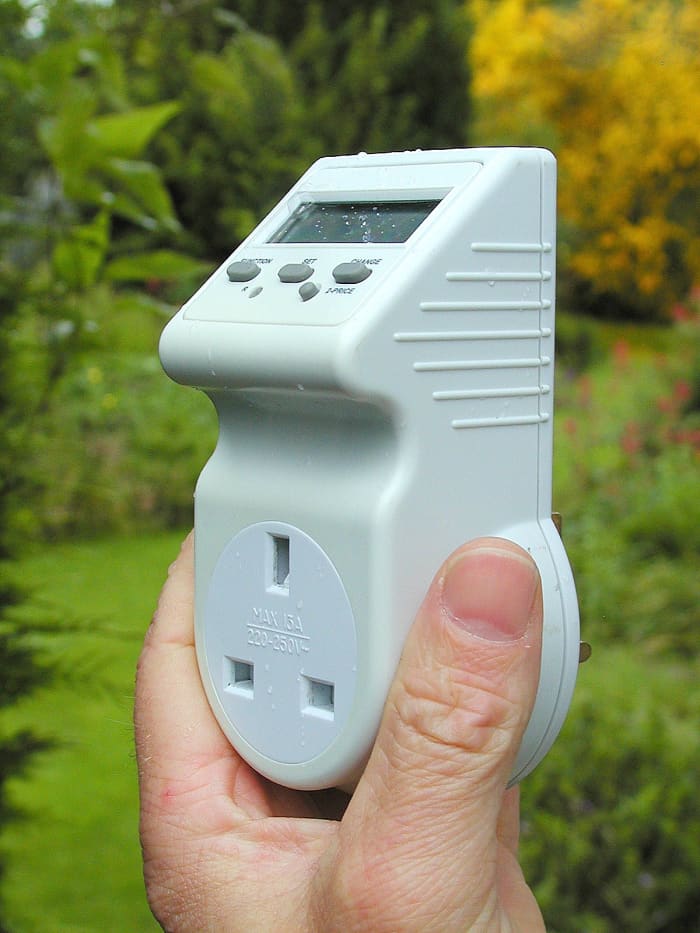

Power adapter. (As well known as an energy monitor/power tracker)
© Eugene Brennan
How to Bank check Superlative Voltages - Using a DVA Adapter
Some meters take a push button which sets the meter to read max and min RMS voltages and/or top voltages (of the waveform). An alternative is to utilize a DVA or Straight Voltage Adapter. Some components such as CDI (Capacitor Discharge Ignition) modules on vehicles, boats and small-scale engines produce pulses which vary in frequency and can exist short duration. A DVA adapter will sample and hold the peak value of the waveform and output it every bit a DC voltage and so the component tin can exist checked to run into whether information technology'south producing the correct voltage level. A DVA adapter typically has two probe leads as input for measuring voltage and either two output leads with banana plugs or a connector with fixed plugs attached for plugging into a meter with standard spaced sockets. The meter is fix to a loftier DC voltage range (e.thousand. m volts DC) and the adapter typically outputs 1 volt DC per 1 volt AC input.
Important data for anyone using a DVA to cheque ignition circuits!
In this application, the adapter is used for measuring the primary voltage of a stator/ignition coil, not the secondary voltage, which could be about 10,000 volts or more.
Fluke also industry meters that can capture the peak level of brusque transients due east.k. - The Fluke-87-five, Fluke-287 and Fluke-289 models.
True RMS Multimeters
The voltage supply to your home is AC, and voltage and current vary in polarity over time. The waveform is sinusoidal every bit in the diagram below and the change of direction of current is known equally the frequency and measured in Hertz (Hz). This frequency tin can exist l or 60 Hz, depending on which country you live in. The RMS voltage of an AC waveform is the constructive voltage and similar to the boilerplate voltage. If the meridian voltage is Vpeak, then the RMS voltage for a sinusoidal voltage is Vpeak / √2 (approx 0.707 times the top voltage). The power in a circuit is the RMS voltage multiplied past the RMS electric current flowing in a load. The voltage normally printed on appliances is the RMS voltage even though this is not usually stated.
A basic multimeter will bespeak RMS voltages for sinusoidal voltage waveforms. The supply to our homes is sinusoidal and so this isn't a trouble. Nonetheless if a voltage is non sinusoidal, e.g. a square or triangular wave, then the meter volition not indicate the true RMS voltage. Truthful RMS meters however are designed to correctly indicate RMS values for all shaped waveforms.
The AC Supply Feeding Our Homes is a Sine Wave
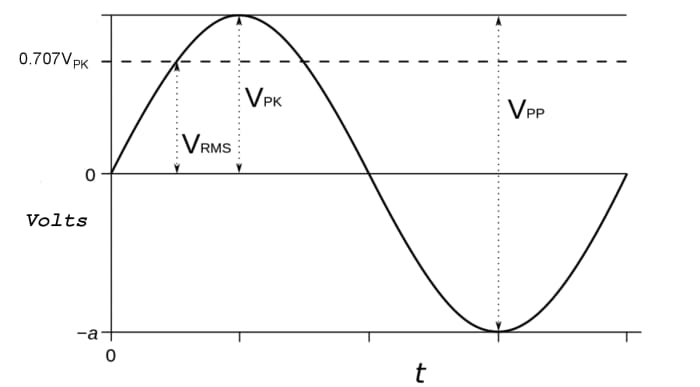
RMS and height voltages of an Air-conditioning sine waveform. Vpp is the peak to peak voltage
AlanM1, public domain epitome via Wikimedia Eatables
Measuring Voltages Remotely and Logging Readings
If you lot need to measure voltages and log them over time, yous tin can use a datalogging multimeter. A product such as the Fluke 289 True-RMS datalogging multimeter can record 15,000 readings. Another characteristic of this meter is that it tin be setup with a wireless connector to communicate with an Android mobile device, allowing readings to be viewed remotely, while the meter is located elsewhere.
FAQs About Multimeters
How Do You lot Check Voltage With a Multimeter?
Plug the black probe into COM and the red probe into the socket marked VΩ. Set the range to DC or Air-conditioning volts and impact the probe tips to the two points betwixt which voltage needs to be measured.
How Do You Bank check if a Wire is Alive With a Multimeter?
For this it's best to stay rubber and utilise a non-contact volt tester or stage tester screwdriver. These will point if voltage is eastward.m > 100 volts. A multimeter can but measure out the voltage between live and neutral or live and globe if these conductors/terminals are accessible, which may not always be the case.
How Do You Check Voltage Drop With a Multimeter?
Voltage drop occurs across a resistance or along a power cable. So follow the same procedure every bit for measuring voltage and measure voltage at the 2 points of interest and subtract one from the other to measure voltage drop.
Why is Voltage Drop Important?
If voltage drop is excessive, appliances may non piece of work properly. Cablevision should be sized adequately to minimise voltage drop for the current it needs to carry and the distance over which current travels.
References
Digital Multimeter Troubleshooting & Solutions. Fluke. (n.d.). https://world wide web.fluke.com/en-us/learn/weblog/digital-multimeters
Digital multimeter: What is the accurateness, range and resolution? (2021, May 9). Fluke. https://world wide web.fluke.com/en-ie/learn/blog/digital-multimeters/accuracy-precision
This article is authentic and true to the best of the author'southward knowledge. Content is for informational or entertainment purposes but and does non substitute for personal counsel or professional communication in business, financial, legal, or technical matters.
Questions & Answers
Question: How do I exam and place faults of three stage system of both command circuit and power circuit for motors?
Answer: Take a look at this document which may assistance:
https://world wide web.schneider-electric.hu/documents/automa...
Question: To be clear, am I correct in my interpretation that if I want to cheque that there is 230v in my electrical connections in a light plumbing equipment that is glowing dimly, I demand the lamp in get-go to complete the circuit, and then I check either finish of the plumbing fixtures placing the meter in parallel? Conversely, if I were to use the meter in lieu of the lamp, then this would exist in serial and the reading would be false or the meter would simply not work?
Answer: If the plumbing fixtures is wired correctly, it doesn't thing much if the lamp is in place or not equally regards measuring the voltage. Yes, you do connect a meter in parallel with a load (i.eastward. the lamp in your case) to measure out voltage. Simply because a lamp doesn't take much current, it doesn't drop voltage significantly. Now if the load was high powered e.g. a heater, the voltage would drib a few volts. The open circuit voltage of a voltage source is always higher than the output voltage on load because a real voltage source e'er has internal resistance, plus the connecting wires accept resistance too. And then if the connecting wires are long or cross-sectional surface area is small-scale, the voltage drop tin be considerable if the wiring is sized inappropriately. If you connect the meter to the plumbing equipment without the lamp, it'due south in parallel with the output terminals on the plumbing equipment and considering it'south ready to "volts", no current flows through it (well actually just a little, but microamps because it has such a high resistance). If the meter was fix to "amps" it would be like a short circuit and effectively in series with the supply and a fuse would blow. Maybe the concept of parallel and series is a bit confusing. Just recollect that when the meter is set to volts, it measures the voltage between two points and when fix to amps, it measures the electric current flowing betwixt the ii points.
© 2012 Eugene Brennan
Collins on Oct 22, 2019:
Useful
Eugene Brennan (author) from Ireland on Apr 03, 2019:
A meter has a very high impedance and sensitivity to voltage. Even though the black isn't connected to annihilation, there is capacitance between the metal probe tip and wire of the black atomic number 82 and ground. Then a minute current can really flow backwards and forwards through the air as this tiny capacitor charges and discharges equally the AC continually changes direction, If you've e'er put your hand on a plasma ball, a discharge flows through the ball to the glass at the point where your hand touches it. This is pretty much for the same reason. Look up capacitors on Wikipedia for more info.
Jay Mengel on April 03, 2019:
I am replacing a ceiling fan. In checking the voltages i find i get a reading of ix - 10 volts when I connect only the red pb of my test meter to the hot wire. The black is not connected to anything. Is there an explanation? If affect the black pb to basis or the mutual wires I go 120 volts (+/- a couple)
Eugene Brennan (author) from Ireland on December 09, 2018:
Thanks Michael for the feedback!
If you lot have any questions virtually multimeters or electricity, simply ask.
Michael Kingston on December 08, 2018:
Having just enrolled on a auto electrical form at Cardiff and the Vale College, Cardiff and no nothing about vehicle electrics. I find your commodity near multimeters fascinating. Give thanks you lot!
Eugene Brennan (writer) from Ireland on November 30, 2018:
Hi Mark, it possibly could. Sometimes adapters aren't regulated and 12 volts output means the voltage it gives on full load, merely this can ascent when off load. A regulated adapter gives a constant voltage, independent of load. If it's an AC adapter, it'south probably just a transformer, without any regulating electronics. 17.4 volts sounds very high though for a 12 volt adapter off load, a volt or two would exist normal.
Does the microscope definitely require Air-conditioning, rather than DC? Without beingness able to load the adapter with a electric current equivalent to what the microscope takes and see if voltage falls, I can't say whether or non it would cause damage.
Mark on November 30, 2018:
I but bought a 12v (written on on it) Air-conditioning adapter. I measured the voltage at the tip of information technology with a Fluke meter. I am reading 17.4v, is this normal? My device (a LED illuminated microscope) requires 12v. Will I damage the LED bulb if I utilize this Ac adapter?
Eugene Brennan (author) from Ireland on Oct 20, 2018:
Only if they're connected to a loftier voltage source. Above about 50 V, a voltage source will begin to produce a sensation. However the intensity and actual threshold level depends on several factors such as location on the body of the indicate of contact, nature of the pare e.grand. smooth or calloused, whether skin is dry or moist etc. An ohmmeter or multimeter set to the ohms range, outputs a voltage and uses this to feed a current through a continued resistance in social club to calculate its value (R = V / I). However this voltage is relatively low. A Megger blazon insulation tester as used for checking insulation quality in electrical installations nevertheless, generates much higher voltages which volition daze.
Mike gordon on October 20, 2018:
Can the probes daze me if I touch them
Eugene Brennan (author) from Ireland on July 23, 2018:
Hi Pranjal. Yeah you can measure AC current if the meter has an Ac current range. The process is the same as for measuring DC current described above. If measuring mains currents, precautions must be taken, including simply not limited to the following:
i Check that probes are non damaged with whatsoever exposed conductors
2 Ready the meter to the appropriate range and make connections with ability turned off
3 If you estimate that the current will be higher than the maximum range, use the loftier electric current setting and utilize the loftier current (due east.1000. 10A or 20A) socket
4 If you don't know the current, simply think information technology may be greater than the value of the highest current range, yous will need to use a clamp meter. The high current range may not be fused.
5 Use a meter with a True cat rating to suit the conditions of measurement
pranjal on July 23, 2018:
sir tin can nosotros check the air-conditioning current using digital multimeter and without clamp meter if yes and so how?
grand.chick. on July 04, 2018:
very, very useful information; fifty-fifty for a 71 year old novice like myself. Thankyou for all the fourth dimension you must have invested in this posting.
Eugene Brennan (writer) from Ireland on June xiii, 2018:
I'm non an electrician, but I presume a "Megger" type musical instrument would be required for testing insulation plus some other for testing globe loop impedance and a 3rd for testing RCDs. Alternatively a multifunction tester to all tests could be used. A multimeter would exist of express use.
MGREEN201 on June 13, 2018:
Thanks Eugene. I have some of them already. Can you advise any decent journal manufactures or published papers .. I realy demand to utilize excessive literature review for my work and would appreciate any suggested sources
MGREEN201 on June xiii, 2018:
I had an electrician who used a multi meter to deport out an EICR ( PERIODIC TESTING ) USING A MULTI METER. I WAS SUPRISED As I DIDN'T THINK IT WAS POSSIBLE HE Assured ME IT WAS. NUT QUESTION IS .IS It POSSIBLE TO Do A Total EICR ( PERIODIC Exam ) USING A MULTI METER.i know for a fact that he couldn't get a tripping time for the rcd
Dinesh on May 30, 2018:
Nice data thanks
Fredrick Mtonga on May 25, 2018:
thank you very much, the notes are cursory I have learned a lot. ..
Eugene Brennan (author) from Ireland on May 09, 2018:
ABF, tin can you explicate this a bit clearer?
ABF on May 09, 2018:
when we mensurate the electric current between two source is not applicative. why?
mintesenot debebe on April 22, 2018:
I have no words that's overnice and brilliant note I wanna say thank you.
bob on March 24, 2018:
very needed -cheers
Eugene Brennan (author) from Ireland on February 04, 2018:
Important! - For anyone using a DVA adapter mentioned beneath. These adapters are for measuring the main voltage of a stator/ignition coil, not the secondary voltage, which could be most 10,000 volts.
Fluke too industry meters that tin can capture the peak level of short transients e.g. - The Fluke-87-v, Fluke-287 and Fluke-289
Eugene Brennan (author) from Ireland on November xx, 2017:
Hello Jabba,
The meter is practically a short circuit when the the leads are connected to measure current. If you connect information technology to a voltage source, it will accident the fuse in the meter. The loftier current range (10A/20A range) may non exist fused on a cheap meter, so the meter will likely exist destroyed if the voltage source tin can potentially supply a large current (the mains or a battery).
Does this respond your question?
jabba on November 20, 2017:
What is the event when testing (electric current) A and the probes are connected to (voltage) V?
Loves chowri on October 10, 2017:
When you say the probe is in open air, are you belongings it, or is it resting on a surface?....
Tsegazeab on August 31, 2017:
How we measure the laptop voltage regulator
Eugene Brennan (writer) from Ireland on August 03, 2017:
How-do-you-do J,
First check the meter reads 0 volts with the probes touched together to confirm there isn't a fault causing it to display an start voltage.
When you say the probe is in open up air, are y'all holding it, or is it resting on a surface?
A digital multimeter has a high impedance, typically 10 megaohms. When ane probe is contacting a 220 volts supply and the other end is in free air, yous finer have a potential divider circuit. A potential divider (Google information technology for more details) consists of a number of resistors connected in series. When the divider is connected to a voltage supply, a reduced voltage is available at the junction between the resistors (an example is the volume command on a radio). In the most simplest of examples, ii resistors of equal value will give one-half the input voltage at the junction. In your case, the meter forms 1 part of the potential divider. The other part consists of the resistance from probe through the air to ground (practically infinite), the resistance from the probe through your hand to ground (could be hundreds of megaohms if there is high humidity) and the reactance of the probe to ground (due to capacitance). The latter 3 are in parallel.
J. Karthikeyan on August 03, 2017:
Digital multimeter ii probes. One probe places in stage 230VAC, another probe placed in open up air. Just meter reading shows 30V. Meter reading is correct? Pls explain.
Don on April 08, 2017:
Verry informative information was a bit dried at present remember many thanks kind regards Don
Rochy/Scientist Sandy. on April 01, 2017:
Cheers very much for such helpful data, I'm passionate with electronics and inventing some cool devices, and my aim is to make complimentary energy/electricity, so my trouble is that I don't know how practice we determine voltage a diode tin can handle similar 1N4008 or 1N540 and Voltage regulator and transistor, my question is how do we determine their voltage rating because some of them are not fifty-fifty written or they're faded and where and in which circumstances do nosotros utilise suppression capacitor, I'd similar information technology if u poke me on my email when u get risk to answer my question and where to follow my respond Makhokha93@gmail.com thank you lot for your noesis.
Eugene Brennan (author) from Republic of ireland on January 25, 2017:
You tin can use a potential divider circuit to mensurate high voltages with a low voltage range meter. In fact this is how the internal circuitry in a meter reduces voltage for the various ranges. However the effort required isn't really worth it. You would also take to build everything into a box so that there are no wires/terminals/components exposed which could cause shock. You tin buy a multimeter for about $10 from Dealextreme or other similar gadget suppliers which volition measure out voltage, current and resistance.
TW on January 25, 2017:
How to utilize a low range voltmeter for loftier voltages
Eugene Brennan (author) from Ireland on October 16, 2016:
Howdy Pascal,
This won't harm the meter (assuming the voltage is less than the rating at the input sockets, typically 600 volts)
An AC voltage is in effect DC for each half of a bicycle, so DC is being practical to the inputs anyway.
Remember when y'all are making a measurement with a meter to set up the range start before you connect the probes to the voltage under test.
When measuring current, a meter usually has two current sockets. The lower current socket is normally fused, but the college current socket may or may not be fused. If you gauge the electric current being measured volition be higher than the value indicated on the lower electric current socket, connect the probe to the college current socket, otherwise you'll nd up blowing a fuse.
Promise this helps!
pascal on October xvi, 2016:
hi I have a question suppose that I desire to measure out a DC voltage and I mistaken I indicate the rotary to AC . what volition I practise?
Eugene Brennan (author) from Ireland on November 08, 2014:
How-do-you-do "lost",
by test leads being damaged, I mean whatsoever insulation scuffed, peeled back or cut to the extent that the inner copper cores are exposed and liable to be touched. As well insulation tin can crack, and leads pull out from the probe or plug end of the examination atomic number 82, once again exposing the conductor. I call up I take a damaged prepare of leads, so I'll upload a photo.
I'll add explanations with graphics of series and parallel connections. Let me know if annihilation else needs explaining.
lost on Nov 08, 2014:
Very Proficient info , can you explain what some of the things are for people like myself that are Very Very unfamiliar with the terminology ? In the safety first lonely I was lost on leads not being damaged , (peradventure a picture show glossary of lingo) or what a series or parallel is etc. love this hub ,merely from my lack of certain words or terms and their pregnant I was lost from the beginning. Give thanks You
Source: https://dengarden.com/home-improvement/Using-a-Multimeter